Business analysis is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. It requires a combination of technical skills, such as knowledge of business processes, systems, tools, and techniques, as well as soft skills, such as communication, collaboration, problem-solving, negotiation, attention to detail, and teamwork.
While technical skills are essential for performing the tasks and activities of business analysis, they are not enough to ensure success in this role. In today’s fast-paced and complex business environment, where change is constant and uncertainty is high, business analysts need to have strong soft skills that enable them to interact effectively with others, understand their perspectives, influence their decisions, and manage their expectations.
In this blog post, we will explore why soft skills and communication are crucial for business analysis talent, what are some of the most important soft skills that business analysts should master, and how you can develop and apply them in your organization.
Why are soft skills and communication important for business analysis talent?
Soft skills are the personal attributes and abilities that allow individuals to effectively interact with others in a professional setting. They include:
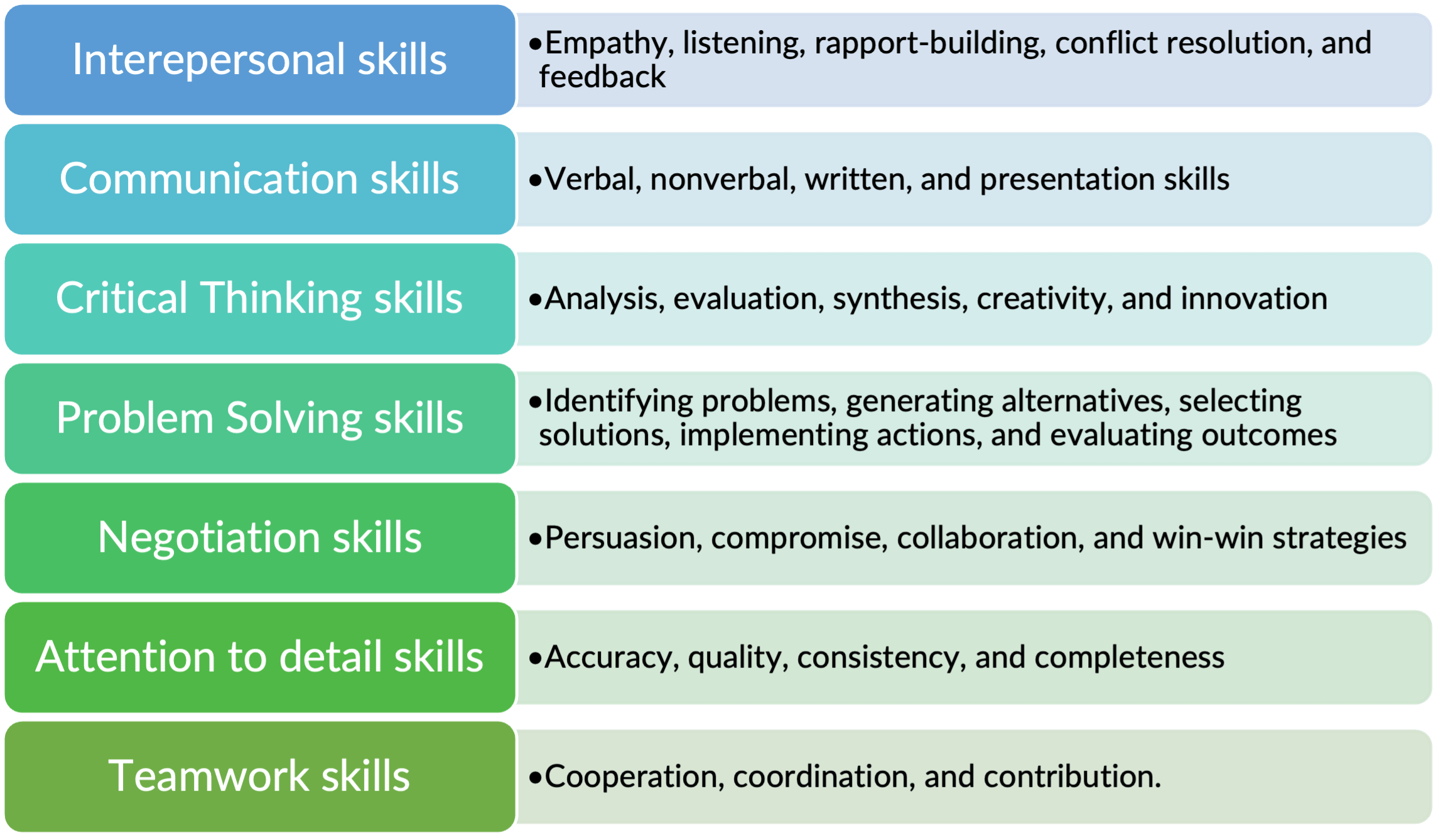
Communication is essential for building strong relationships with colleagues, clients, and stakeholders, which is especially important when working with teams. Effective communication skills can help foster collaboration, trust, and mutual understanding among team members, as well as improve the quality and efficiency of the work output. Communication also enables team members to share their ideas, feedback, and perspectives, which can lead to innovation and creativity.
Soft skills and communication are important for business analysis talent for several reasons:
- They help business analysts understand the context and environment of the problem or opportunity they are trying to solve or exploit. They enable them to gather relevant information, identify key stakeholders, understand their needs, expectations, and preferences, and align them with the organizational goals and vision.
- They help business analysts communicate the results of their analysis and recommendations to various audiences, such as technical teams, business users, senior management, and external partners. They enable them to tailor their messages to suit different levels of understanding, interest, and influence, and use appropriate formats, such as documents, diagrams, models, or presentations.
- They help business analysts collaborate with others to deliver solutions that meet the needs of the stakeholders and add value to the organization. They enable them to work effectively in teams, share ideas, give and receive feedback, resolve conflicts, negotiate agreements, and implement changes.
What are some of the most important soft skills that business analysts should master?
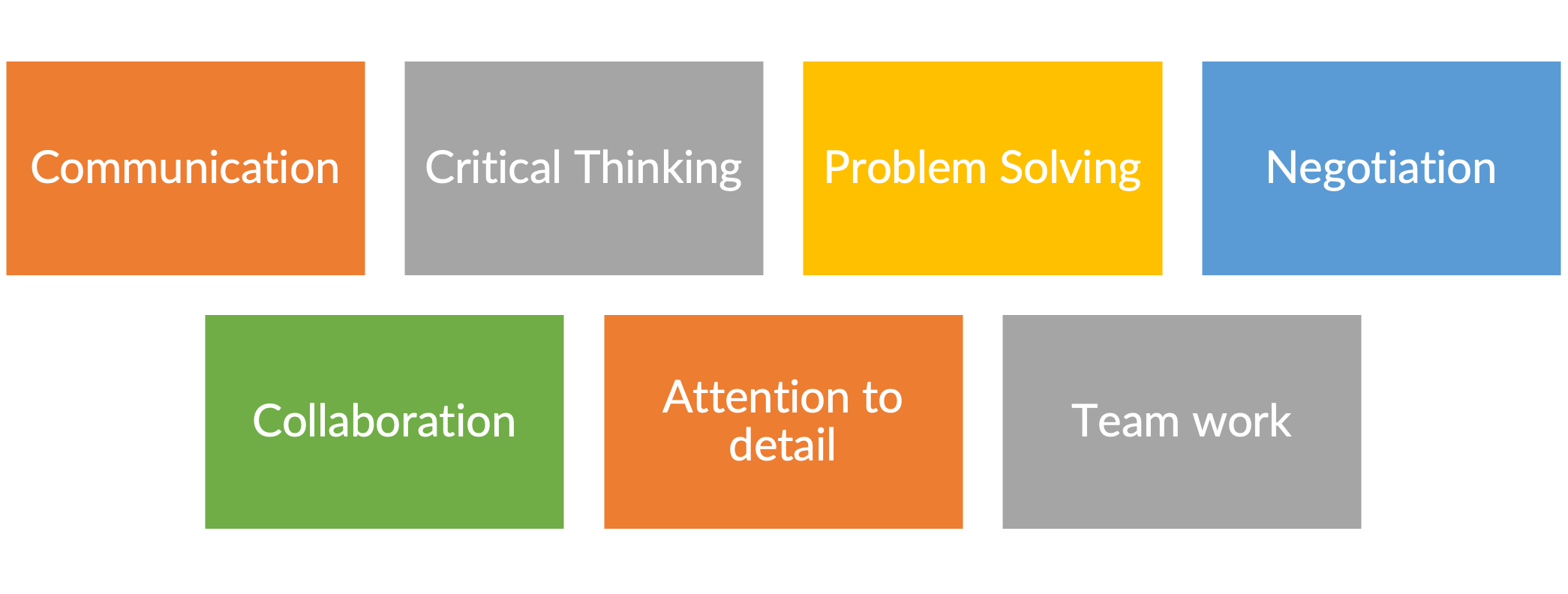
Let’s look at each of these skills in more detail and see how they can be applied in different scenarios.
Communication skills play a vital role in every stage of a business analyst’s work.
During the elicitation stage, they utilize active listening and verbal communication skills to Conduct interviews, workshops, surveys, or observations with stakeholders. This helps them gather requirements, needs, and expectations effectively.
In the analysis stage, business analysts employ written communication skills to document their findings, assumptions, constraints, and risks in various formats such as business requirements documents (BRDs), use cases, user stories, or functional specifications.
In the validation stage, presentation skills are essential as business analysts communicate their analysis and recommendations to diverse audiences like technical teams, business users, senior management, or external partners, while soliciting feedback and approval.
Critical thinking is another vital skill for business analysts throughout their work.
During the elicitation stage, analysts use analysis skills to identify root causes and understand the context and environment of the problem or opportunity at hand.
In the analysis stage, they employ evaluation skills to assess the feasibility and viability of different solutions or alternatives, comparing them against stakeholder criteria and constraints.
During the validation stage, synthesis skills come into play as analysts present their analysis and recommendations in a clear and compelling manner, highlighting the benefits and value proposition of their proposed solution.
In the implementation stage, business analysts leverage creativity and innovation skills to support solution execution and monitor its performance and impact.
Problem-solving skills are crucial for business analysts in every stage of their work.
During the elicitation stage, analysts use problem identification skills to define project scope, objectives, and establish baseline and target states.
In the analysis stage, they employ alternative generation skills to explore different options or scenarios for achieving desired outcomes, considering assumptions, risks, and dependencies.
During the validation stage, solution selection skills help evaluate and prioritize options based on feasibility, viability, and desirability, enabling them to recommend the optimal solution or approach. In the implementation stage, action implementation skills are essential to plan and execute tasks and activities required for delivering the solution, managing changes and issues.
During the evaluation stage, outcome evaluation skills enable analysts to monitor and assess the performance and impact of the solution, identifying gaps or opportunities for improvement.
Negotiation skills are vital for business analysts throughout their work.
During the elicitation stage, preparation skills help gather information about stakeholders, their needs, preferences, and level of influence.
In the analysis stage, rapport-building skills establish trust and rapport with stakeholders through empathy, respect, and rapport-building techniques.
During the validation stage, persuasion skills are utilized to influence stakeholders to accept analysis and recommendations, using logical arguments, evidence, emotional appeals, or ethical principles.
In the implementation stage, compromise skills aid in finding a middle ground between analysts’ position and that of stakeholders, through concessions, trade-offs, or incentives.
Collaboration skills are necessary during any stage, allowing analysts to work together with stakeholders, focusing on interests rather than positions, generating creative options, and using integrative bargaining techniques. Closure skills are required to finalize and formalize agreements, summarizing main points, confirming mutual understanding, addressing remaining concerns, and documenting agreements.
Attention to detail ensures accuracy, quality, consistency, and completeness in a business analyst’s work. During the elicitation stage, organization skills help plan and prioritize elicitation activities, manage time and resources, and follow standards and guidelines.
In the analysis stage, accuracy skills ensure precision and correctness while avoiding errors or omissions.
In the validation stage, quality skills deliver analysis and recommendations with high standards, meeting or exceeding stakeholder expectations. Consistency skills maintain a uniform style, format, and tone in the work, ensuring alignment and compatibility with other related works or products.
Completeness skills are vital in the evaluation stage, providing all necessary and relevant information, data, or documentation without gaps or ambiguities.
Lastly, teamwork skills are essential for business analysts in every stage of their work.
During the elicitation stage, cooperation skills promote effective collaboration with other business analysts, stakeholders, or subject matter experts (SMEs), sharing responsibilities and resources.
Coordination skills are utilized in the analysis stage to align work with other business analysts, technical teams, or project managers, communicating clearly, following instructions, and meeting deadlines.
Contribution skills play a role in the validation stage, allowing business analysts to add value to their team by showing initiative, creativity, leadership, and providing feedback and suggestions.
How can we help you boost your business analysis talent?
At Primed Talent, we are passionate about helping you find, hire, and retain the best business analysis talent for your organization. We understand that business analysis is not just about technical skills, but also about soft skills and communication that make a difference in delivering value to your stakeholders.
If you are interested in boosting your business analysis talent, we would love to hear from you. We would appreciate the opportunity to communicate with you and help you in accomplishing your goals.